02 Sep Pure Tiva™ “Tiva Tab” Technology
Why & How Lipofusion™ Technology Improves Upon Conventional Cannabis/Hemp Oils and Existing Nanoemulsion & Encapsulation Methods to Optimize Bioavailability and Assimilation of Cannabinoids at the Molecular Level
Introduction
The purpose of this overview is to examine and provide a comparative analysis of new technologies and conventional methods for delivering vital cannabinoid nutrients and, more specifically, improve their bioavailability to optimize activity in the human endocannabinoid system.
Bioavailability of cannabinoids has improved significantly over the last decade with the advent of Nanoemulsion technology. However, degrees of efficacy vary based upon the methods used to deliver cannabinoids such as Cannibidiol (CBD). Few technologies have overcome problems of nutrient degradation due to:
• Decomposition and chemical alteration at many levels in the digestive system
• Hydrolysis or breakdown of molecules upon exposure to fluid, in this case, entry into the GI tract
• Bioavailability of active CBD is reduced when taken alone (without food or water)
Tiva Tabs uses a proprietary, patent pending nanoliposomal encapsulation technology called Lipofusion™ that incorporates soluble fibers with nanoliposome vesicles to mitigate bioactive degradation and overcome common obstacles to bioavailability (such as those mentioned above).
Magnesium Intake and Deficiency Prevalence
With so many food choices available today, it may be hard to believe that vitamin or mineral deficiency is possible. Yet, the data shares that, when it comes to magnesium, is it more than possible. It is actually probable.
The Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) reports that 48% of Americans have a low magnesium intake. Additionally, low intake levels are more common among certain populations. This includes men 71-years-old and older, while also being low in teens.
Fortunately, our kidneys are good at controlling magnesium levels. It does this by dictating the amount of magnesium released in our urine. As a result, magnesium deficiency is not very common, even with low intakes. Though, some people are more at risk of a magnesium deficiency. This includes those with gastrointestinal disorders. Individuals with type 2 diabetes or abnormal kidney function are at risk too.
Magnesium deficiency may also occur due to prescription medications. One study reports that diuretics and proton-pump inhibitors are among the most problematic. The ODS adds that antibiotics can be an issue too. Chronic alcoholism can also lead to being magnesium deficient.
The Evolution of CBD Delivery
Scientists have identified 66 major cannabinoids present in all varieties of the cannabis plant, each serving a variety of medicinal/therapeutic purposes by working synergistically to activate key functions of the human endocannabinoid system. These cannabinoids fall into several subclasses including cannabigerols (CBG), cannabichromenes (CBC), cannabinols (CBN), cannabicyclol (CBL), cannabielsoin (CBE), cannabitriol (CBT), cannabidiols (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinols (THC), among others that are lesser known. The most commonly known and extracted cannabinoids are THC, which produces the psychoactive effect of “marijuana” and CBD, which is found in abundance in the hemp plant.
Until recently, available delivery methods of cannabinoid actives were limited to:
• Cannabis flower, commonly smoked and baked into edibles to decarboxylate (activate) THC
• Inhaling vaporized extracts
• Pressed oils and extracts, which can be taken orally or applied topically to the skin
In the last decade, cannabis supplement manufacturers have developed more precise methods of extracting the bioactive compounds and isolates.
Utilizing nanoemulsion technology, manufacturers have successfully facilitated improved uptake and bioavailability. However, most recently, nanoliposomal encapsulation technology has emerged as a more effective delivery method that makes therapeutic CBD even more bioavailable within the body.
What is a nanoliposome?
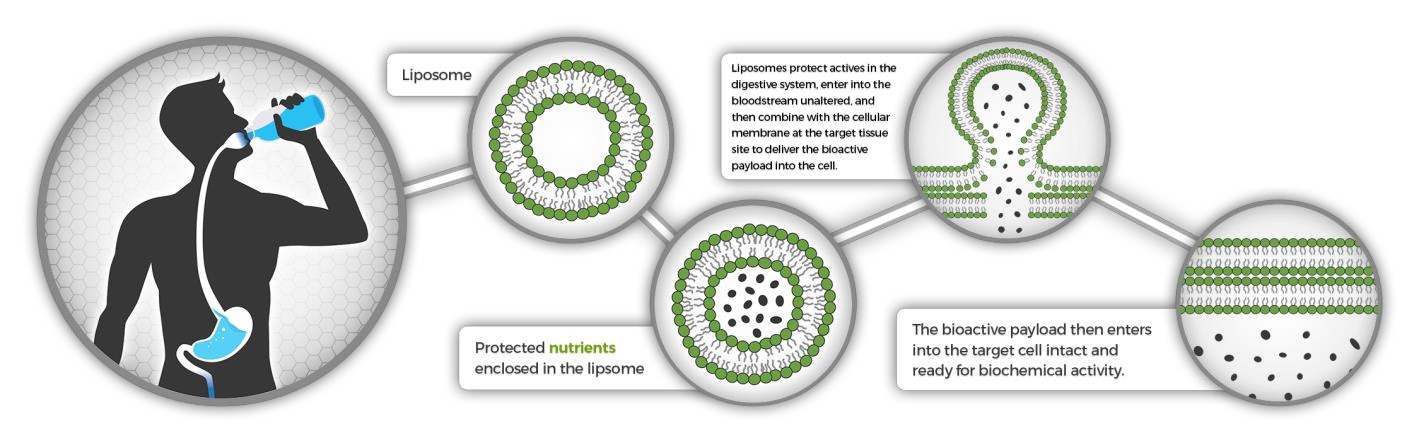
The word “liposome” is derived from two Greek words: “Lipos” (which means fat) and “Soma” (which means body). Liposomal technology isn’t new and has been around since the 70’s. It’s most commonly used by hospitals in the form of intravenous and intramuscular medicine. The prefix ‘Nano’ denotes that the liposome size is submicroscopic.
A liposome is a spherical vesicle resembling a cell with an outer shell comprised of fat-soluble phospholipids that protect the water and fat-soluble actives inside from degradation while en route to their destination. Since these phospholipids are bioidentical to our cell membranes, this outer “shell” functions the same way a human cell membrane does to protect its molecular center and inner compartments.
One of the most important functions of phospholipids is to protect and regulate the transport of nutrients through the small intestine and into the blood stream targeting your cells. In this capacity, these molecules work as ‘gatekeepers’ and play an integral role in determining what goes in and out of the cell.
How does nanoliposomal delivery supercharge bioavailability?
The key to nanoliposomal delivery is in the protective layer of the nanoliposome’s phospholipids. First, it is important to understand the structure of phospholipids, as this holds the key to grasping how nanoliposomes work.
In layman’s terms, each phospholipid molecule is made up of a circular “head” which likes water and a “tail” that does not. The heads are attracted to water while the tails try to avoid it, causing the
phospholipids to arrange themselves in double layered lines where the heads are all outside, touching water, and the tails are “dry” in the encasement they’ve created.
In an aqueous solution (i.e. water), the phospholipids automatically self-assemble into a double layer so the hydrophobic fatty acid tails (which like to stay dry) move away from water and turn inward; whereas the water-loving phosphate head moves toward the liquid by turning toward the middle of the double layer. This results in a closed, spherical structure called a “nanoliposome” with a hollow aqueous core surrounded by a double-layer (bi-layer) membrane, which encapsulates active CBD and other nutrients into these microscopic vesicles and protects them from digestive degradation and hydrolysis in the bloodstream until they are fused into the cells.
Other functions of phospholipids:
• Allow cell membranes to be fluid, which helps cells to change shape, fuse with one another and adapt to environmental changes
• Mimic our own cellular molecules to enable assimilation at the cellular level (for example, phospholipid molecules can bypass white blood cells without signaling an immune response (such as attacking a foreign pathogen or targeting the site of infection)
• Protect cell membranes against oxidative damage caused by free radicals
• Enable fusion of active nutrients through membranes of targeted cells at the molecular level
Comparative analysis of conventional, nano-emulsion, and nanoliposomal delivery technology
Conventional Supplements:
The contents of conventional supplements undergo decomposition at many levels in the digestive system, thus resulting in wasted nutritional value. Studies have shown that most nutritional supplements taken orally lose up to 90% of their nutritional value during the digestive process.
The body’s digestive system is designed to release enzymes that break down food to extract nutrients from food. While it works well to break down food for absorption, the destructive nature of the digestion process can degrade the vulnerable, microscopic actives in nutritional supplements before the body gets a chance to assimilate them. This can greatly limit effectiveness and decrease nutritional value of the supplements.
Nutrients carried or encased with binders that help them to survive digestion long enough to enter the blood stream can be subject to attack by the white blood cells, which seek to destroy foreign substances in the course of normal immune responses. These factors can also reduce the absorption rate and bioavailability of actives, resulting in wasted nutritional value.
Nanoemulsion Supplements:
Supplements and drugs utilizing nanoemulsion and encapsulation technology to deliver nutrients can vastly improve absorption and bioavailability over conventional delivery methods. However, if they are not encapsulated with fat-soluble outer coatings, they can be unstable and equally vulnerable to degradation upon exposure to digestive enzymes and phagocytic action.
In fact, encapsulating supplements with single layer membranes instead of phospholipids doesn’t protect
the supplements at all. They are immediately absorbed wherever they enter, making it difficult to sustain proficient delivery of actives. Some nanoparticles also trigger an immune response from white blood cells which decreases the amount of time the nutrients stay potent within the body. This is referred to as the
(half-life) which measures the concentration of a substance in the body.
**The most interesting and beneficial innovation of our patent pending Lipofusion™ technology is that our vesicles utilize a nanoliposomal encapsulation process to encase CBD actives within phospholipids that are bio-identical to the membranes that surround human cells. This allows the nanoliposomes to easily target cells on a molecular level, delivering nutritional payloads directly to the bodily tissues that need them.**

